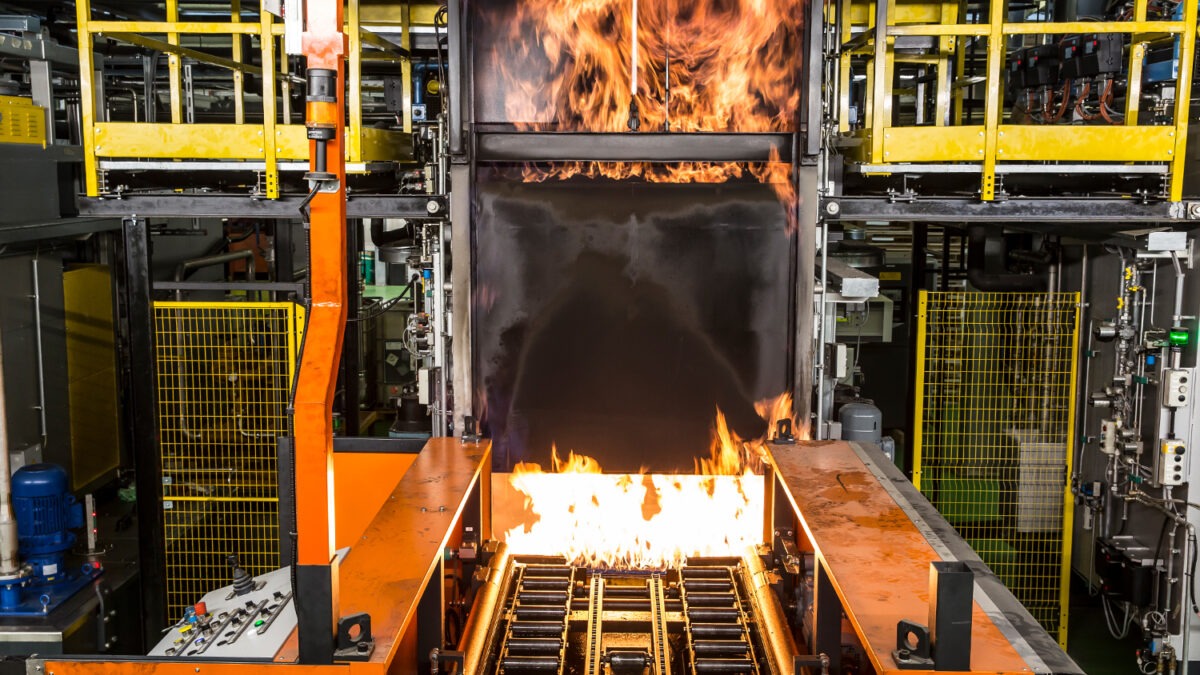
Case hardening / carbonitriding
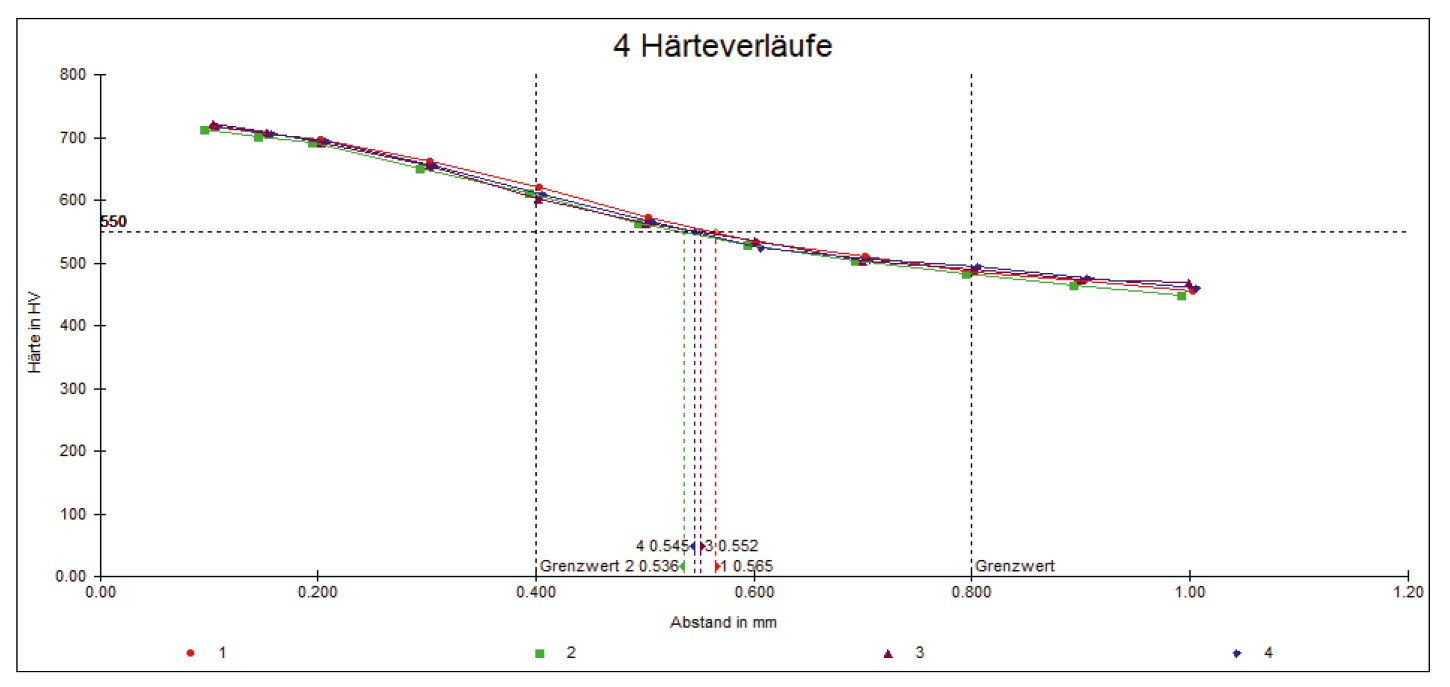
Case hardening is mainly used where high wear resistance is to be achieved on the surface of components. Case hardening or carbonitriding with deeply alloyed material is also a good alternative to tempering with alloyed material. In some cases, the same functions are achieved, but with clear cost benefits, in particular through less tool wear in the preliminary processes such as punching or cold forging. Carbonitriding with small dispersion of the case hardening layer and maximum surface wear resistance is used for thin wall thicknesses to avoid cure through hardening.

Ferrite + pearlite structure with the typical phase course from cold forming